Guide to Treatment-Resistant STDs for Active Adults

Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can be a source of stigma and embarrassment, and, unfortunately, this often keeps people from getting the care they need to stay healthy.
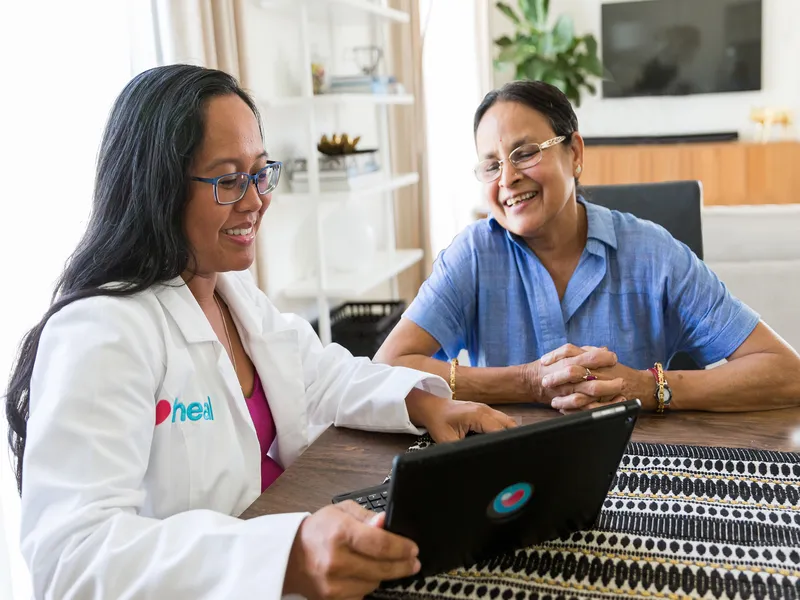
Our providers at All Day Medical Care Clinic offer STD testing in a safe and judgment-free environment. And, while sexual health may not be easy to talk about, you can be assured that you’ll find kindness, compassion, and professionalism during every visit.
If you engage in any sexual activity, whether it’s oral, vaginal, or anal, here’s what you need to know about treatment-resistant STDs and how to avoid them.
What makes an STD “treatment-resistant”
To start, a wide range of diseases and infections spread through sexual contact. They typically fall into two categories: curable and incurable.
Generally speaking, medicines can often cure STDs that are caused by bacteria, yeast, or parasites. Examples of these infections include:
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhea
- Chlamydia
- Trichomoniasis
STDs considered incurable often develop because of a virus. Those infections stay in the body forever, but the virus can become dormant (no longer active). Viral STDs include hepatitis B, herpes, human papillomavirus (HPV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
While this breakdown is fairly straightforward, a new challenge has emerged in recent years. Some STDs that once responded to antibiotic drugs have become increasingly resistant to them.
This change, known as “treatment-resistant” STDs, means that some previously treatable STDs are becoming more challenging to treat despite existing medications. The three most common STDs in this category are gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis.
Prioritizing your health
Studies show that approximately 68 million people have STDs in the United States — not including unreported infections — and 20 million new cases are diagnosed each year. Among those cases, half affect people ages 15-24.
So, if you’re sexually active, there are some things you should do to help protect yourself and stay healthy.
Use protection
One way to help protect yourself from STD exposure is to use male and female condoms, whether you have oral, anal, or vaginal sex.
Unlike other forms of birth control, plastic and latex condoms provide a barrier that limits skin-to-skin exposure and helps prevent contact between vaginal fluids and semen. This form of protection can reduce your exposure to most STDs, including chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, syphilis, and HIV.
Get Tested
The fact is, 1 in 5 people have an STD, and many don’t cause noticeable symptoms. Because of this, it’s essential to make regular STD testing part of your self-care regimen. We offer personalized recommendations on a case-by-case basis, but you should plan on testing:
- When starting a new relationship
- If you or your partner have multiple partners
- When considering not using condoms, dental dams, or other barriers
- If a partner cheats on you
- When you have signs of an STD or learn a partner was infected
- If you use intravenous drugs and share s
Have you been tested lately? If not, get professional, compassionate care by booking an appointment online or over the phone with All Day Medical Care Clinic today.