How Mental Health Issues Affect Men Differently
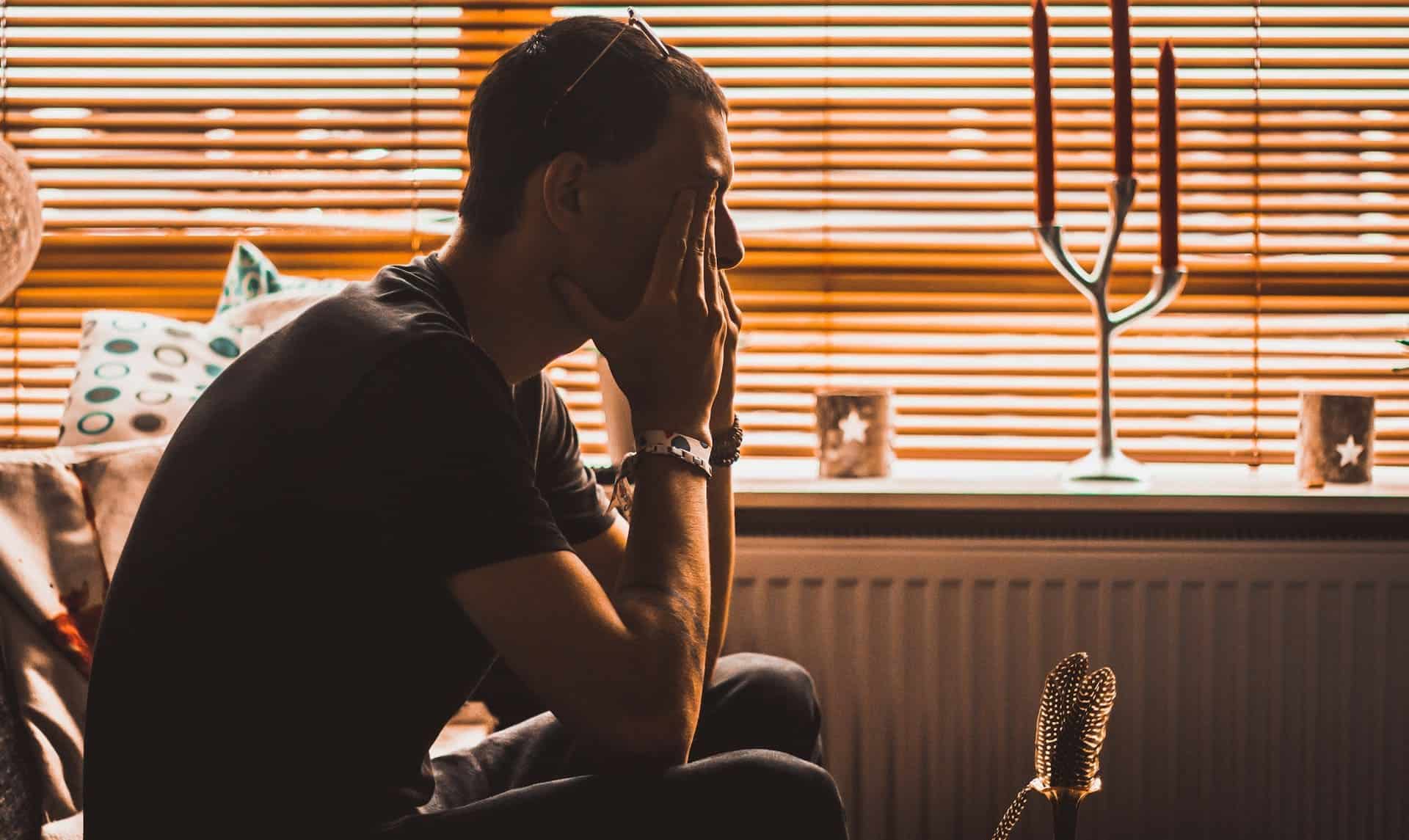

Men’s mental health issues affect them differently due to various societal, biological, and cultural factors. Men are often expected to be resilient and strong-willed, discouraging them from expressing vulnerability or seeking help. This can lead to internalizing struggles and not addressing mental health concerns. Men may also exhibit different symptoms; for example, depression in men often manifests as irritability, anger, or aggression rather than sadness.
The stigma surrounding men’s mental health can further discourage men when they seek the help they need, leading to prolonged suffering and potentially severe consequences. Understanding these differences is crucial for providing effective mental health support tailored to men’s unique experiences.
According to the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention (AFSP), men are almost 3.5 times more likely to be suicide victims than women, with over 75% of suicides in the U.S. being men. The statistic regarding only 36% of psychological treatment referrals being for men is less commonly cited and may vary by source. A similar point about men being less likely to seek mental health services is discussed in reports by the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH).
Who Men Speak to About Their Mental Health
Societal norms that emphasize stoicism and self-reliance often lead to men’s unwillingness to discuss their mental health issues. These factors can make it difficult for men to open up about men mental health, leading to reliance on specific support networks when they do decide to seek help.
Friends and Family: Many men initially turn to close friends and family members. These trusted individuals offer a safe space for men to voice their feelings without any fear of censure.
Professional Help: Men can discuss their problems with professional therapists or counselors without fear of disclosure. Although men are less likely to seek professional help than women, this trend is slowly changing as awareness grows.
Support Groups: Peer support groups, both in-person and online, allow men to share experiences with others facing similar challenges. These groups can be particularly beneficial in normalizing discussions about mental health.
However, men’s mental health statistics from the Canadian Institute of Mental Health show that more than 40% of men are discouraged from discussing their psychological problems. More than 74% of men have never consulted a psychologist.
A study has shown that stereotypes about men trying to put their feelings into words can be true. So many men are nervous about talking frankly because they think they look weak.
What are the barriers to men’s mental health? About 19% of men find it easier to reveal their emotions in a recorded conversation than in person. The researchers also found that partners are the people men feel most comfortable opening up to, but they find it much harder to have meaningful conversations with parents and coworkers.
Why Men Don’t Talk About Their Mental Health
Why is men’s mental health month ignored? Practically from the very childhood, children are divided into boys and girls, not by gender, but by behavior. From a young age, they are taught that a man must be brave and strong, despite external circumstances. He should not show his weakness or cry to those around him. A man is a concrete wall behind which you can always hide. Complaints are the fate of the weak.
That is why most of the representatives of the strong half of humanity avoid visiting doctors because they are ashamed to complain about migraines and signs of mental illness in men. They are sure that it is worth telling about the presence of the problem, as you will be labeled a loser and complainer. A man is afraid to appear weak, especially when surrounded by other men, because it can shake his image and self-esteem. Even if a man feels that from the emotional load will soon snap, he tries to hide it, translating everything into a joke or showing indifference.
All these moments – from education to the propaganda of male pride, make a man hide his own emotions to feel more significant and create an image of a strong man for society. It is still difficult for men to admit to psychological problems, despite the fact that society has changed a lot over the past 40 years. After all, they have no confidence that their loved ones will support them and not stigmatize them as weak.
Warning Signs
Men are often less likely to talk about their mental health than women. This can make it difficult to recognize the signs of a problem. However, some warning signs can indicate a man is struggling with his mental health. How mental health issues affect men differently? These are a couple of critical fields to pay attention to:
Emotional changes:
- Increased irritability or anger
- Feeling withdrawn or isolated
- Frequent sadness, low mood, or tearfulness
- Loss of interest in hobbies or activities
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
Behavioral changes:
- Changes in sleep patterns (sleeping too much or too little)
- Increased alcohol or drug use
- Changes in eating habits (overeating or loss of appetite)
- Reckless or risky behavior
- Difficulty maintaining relationships
- Thoughts of self-harm or suicide
Physical changes:
- Fatigue or lack of energy
- Headaches or body aches with no physical cause
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Loss of sex drive
It is important to remember that each man may have his own set of symptoms, as much depends on the man’s character and behavior. Not everyone who experiences some of these signs will have problems with men’s mental health. A comprehensive mental health assessment is useful for accurately diagnosing and treating various psychological conditions.
Common Mental Health Conditions in Men
Quite often, a man is associated with a strong character, iron will, and lack of emotions, but he is just the same person as a woman, with his feelings and emotions. The fact that he tries to hide them does not mean that they are absent. Men, unfortunately, are very often the victims of approachable mental disorders, and trying to deal with them alone almost always loses the battle.
Depression
Depression appears in different ways in men. The most common symptoms are mood swings, hopelessness, and loss of interest in everyday tasks. You can also notice changes in eating and sleeping habits, a man has trouble with concentration, and he is increasingly haunted by thoughts of suicide. Depression can also cause irritability and anger, and some men are constantly in search of adrenaline and risk their lives.
Anxiety disorders
Men face anxiety disorders. Depending on the situation and personality traits, most men have panic or social anxiety disorder. Usually, these problems can manifest themselves not only in excessive fear and anxiety but also in physical symptoms such as shortness of breath and tachycardia.
Substance use disorders
How mental health issues affect men differently? Men are more likely than women to suffer from substance use problems, including alcohol dependence and drug addiction. Substance abuse may be a coping mechanism for other underlying mental health issues.
Suicidal thoughts
Men may exhibit suicidal thoughts and may be more likely to engage in risky behaviors, such as increased alcohol or drug use, or suicide attempts.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Men who have experienced trauma, such as war or violent events, are at higher risk for developing PTSD. Symptoms include flashbacks, nightmares, trigger avoidance, hyper-vigilance, and emotional numbness.
It is important to remember that men’s mental health disorders can manifest differently and require an individualized approach to diagnosis and treatment. The earlier a man seeks help, the greater the chances of successful treatment and improved quality of life.
Types of Treatment
Remember, you are not alone. Many men experience mental health conditions, and there are different treatments for mental health conditions. Believe in your strength, trust your doctor and mental health problems can be fixed.
Therapy
Most providers recommend cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). The main goal of cognitive behavioral therapy is to overcome stereotypical thinking in men by empowering them to express their feelings and emotions frankly. In addition, CBT also offers a focus on learning healthy coping techniques.
Interpersonal therapy (IPT) helps a man learn how to socialize with people and improve relationships with family and friends, which can be especially helpful for men struggling with depression or anxiety related to relationships.
Group therapy aims to create the most comfortable conditions for men so that socializing with others who understand their problems and offer support and encouragement will be most effective.
Medication
Antidepressants can help regulate brain chemicals that play a role in mood regulation. They can help treat men’s mental health disorders.
Anti-anxiety medications can help reduce symptoms of anxiety, such as racing thoughts, physical tension, and panic attacks.
Mood stabilizers are most often prescribed for men with bipolar disorder to regulate their mood swings.
Lifestyle Changes
The way of a man’s life is of great importance. It is necessary to try to change it for the better. Sleep, its quantity and quality strongly influence a person’s emotional balance. Therefore, to improve your condition, you should review your sleep habits and try to regulate this aspect.
It is necessary to include moderate physical activity to cope with men’s mental health issues, it will help to distract from problems and maintain the health of your body.
A balanced and healthy diet is also essential, as our mood depends on what we eat. Yes, food can affect our mental health, so it is worth giving up bad habits and making a healthy and nutritious menu.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Practices like meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, mindfulness and well-being can help manage stress and improve overall mental health. Even 10 minutes a day will be enough to get your thoughts and feelings in order.
Family Therapy
Family members can be participants in therapy, to improve the effectiveness of the treatment. They will be his best source of support and help him overcome his difficulties. This will help him realize that he is not alone, help him believe in his own strength and motivate him. The support of family members is very important, as well as their understanding. Professional counseling can provide effective strategies to help with anger issues, improving emotional regulation and overall well-being.
How to help
Helping with men’s mental health issues involves creating a supportive environment and encouraging them to seek professional help. Start by fostering open communication, letting them know it’s okay to discuss their feelings without judgment. Encourage professional support and treatment options for mental illness, and emphasize that seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
Take care of yourself and try to stick to healthy habits. Our mental health is very sensitive to all external factors, so do not ignore the first alarm bells, and promptly help to correct the situation. Offer to assist with practical matters, such as scheduling appointments or finding resources. Educate yourself and others about mental health to reduce stigma and increase understanding. Finally, be patient and persistent, recognizing that recovery is a process that requires time and effort. Consistent support can make a substantial difference in helping men manage and overcome mental health challenges.
Conclusion
Men often face unique challenges with mental health, such as societal pressure to appear strong, leading to underreporting and untreated issues. Recognize these differences and take action by encouraging open dialogue, supporting professional help at All Day Medical Care Clinic with men’s mental health disorders, and breaking the stigma. Your support can make a crucial difference. Reach out today.