What is Common Cold?

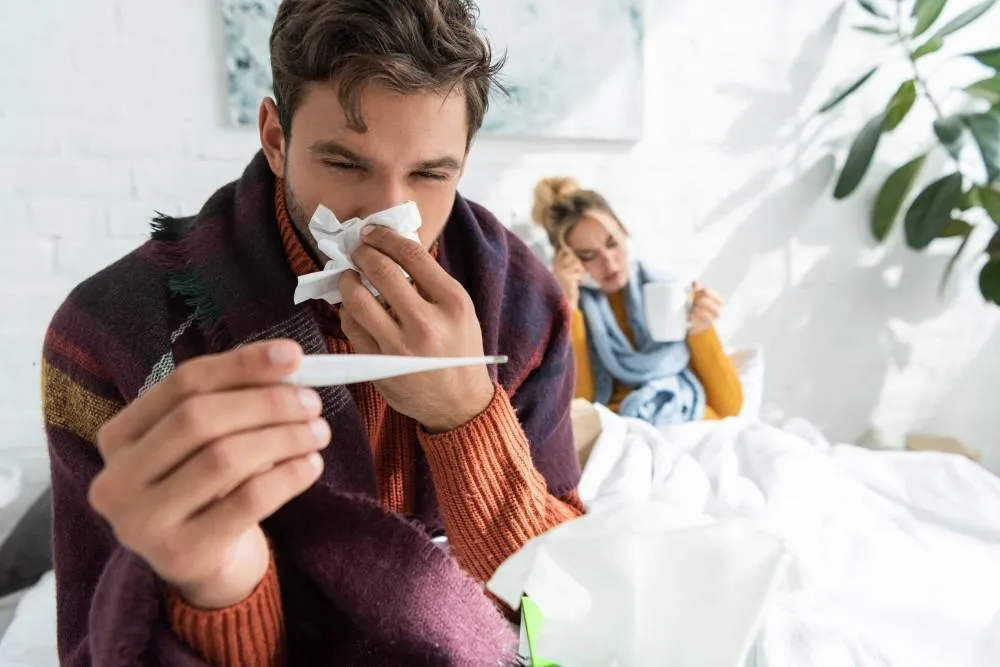
Common cold illnesses tend to affect the upper parts of the respiratory tract, mainly the sinus cavities and throat. Cold vs flu symptoms are very similar, but some variations persist. Colds can be easily transmitted from one person to another, particularly in closed settings like households, classrooms, daycare facilities, and workplaces. A common cold can be caused by roughly 200 viruses or more. It does not need any special therapy and generally subsides within a week to ten-day period.
Everyone has experienced the unpleasant symptoms of a cold vs flu: runny nose, sore and “scratchy” throat, increased body temperature, general weakness. Symptoms of the common cold reduce efficiency and change plans: unpleasant condition forces you to stay at home, putting life on pause. Adults get colds at least 3-4 times a year, and children even more often: up to 5-8 times. Understanding the difference between flu and COVID is essential to ensure proper treatment.
Causes of the Common Cold
In most cases, the patient identifies his disease with a chill, more often in winter. Yet hypothermia is just a provoking factor, the second one after the reduction of immunity and the illness some more developed. In case of physical stress, the secondary infection with bacteria or viruses occurs, and the first cold vs. flu symptoms appear.
The basis of colds is always a decrease in immune status, or more precisely, the lack of immune defense cells in the place of pathogen accumulation.
A combined infection often occurs when viral disease violates the mucous membrane barrier function, leading to the multiplication of opportunistic bacteria, which always live there in small quantities.
Provoking factors that reduce immunity:
- poor nutrition with a deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- overwork;
- nervous stress;
- lack of sleep;
- the presence of chronic diseases;
Symptoms of the common cold often occur in the cold season, when the body is weakened by the lack of sunshine and nutritious fruits and vegetables, and people spend most of the day in closed rooms.
Common Cold Symptoms
How long does a cold last? Typically, it progresses through three distinct stages over the course of 7 to 10 days. Understanding these stages of a cold can help manage symptoms and speed up recovery.
Stage 1: Early (Days 1 to 3)
The symptoms of a cold in the early stages are subtle but noticeable. You may experience a scratchy throat, mild sneezing, and a runny or stuffy nose. Fatigue and slight body aches can also appear as the virus takes hold. At this point, your body is beginning to mount an immune response.
Stage 2: Active (Days 4 to 7)
The active stage is when the symptoms peak and are at their most intense. Nasal congestion worsens, accompanied by a persistent cough, thicker nasal discharge, and sinus pressure. You may feel fatigued and experience muscle aches or headaches. Some people may develop a low-grade fever. This is the most uncomfortable phase of the cold. Stages of the flu are the same, but symptoms are harder.
Stage 3: Late (Days 8 to 10)
By this stage, the body is beginning to recover from the infection, and symptoms start to fade. Coughing may linger, but nasal congestion typically clears up, and energy levels begin to improve. Although you might still feel fatigued, you’re likely on the road to recovery and symptoms of the common flu are gone.
Cold vs. Flu: Key Differences
It’s often tricky to understand whether it’s a cold or the flu since almost all symptoms appear the same. Both diseases are more or less very common in cold seasons and affect the upper respiratory tract. Nevertheless, the newer influenza infection is different from upper respiratory tract infection viruses. The flu is caused by the influenza virus, whereas the coryza can be caused by many different types of viruses.
The main factor that distinguishes flu from colds is that flu is usually accompanied by a high fever, which lasts from 3 to 5 days and can be around 38-39 degrees or even higher.
The extreme depression experienced with the flu may last for weeks. Cold vs flu symptoms tend to be milder and last about 1 week. Also, runny or stuffy nose and sore throat are more common with colds than flu.
Although colds and flu have some differences, it is impossible to know for sure if it is the flu or a cold without special tests. That’s why people always have many flu season questions.
How the Common Cold is Spread
The incubation period is 1-4 days. Airborne droplets transmit the common cold through coughing, sneezing, or dirty hands through direct contact or household objects. It is dangerous to catch the symptoms of the common cold if you have a weakened immune system, and the source of the respiratory infection is in proximity. If the concentration of the pathogen in the surrounding air is low (the room is well-ventilated, the air is sanitized, and carriers of infection are at a decent distance from you), and your immune system is normal, you are not threatened by the disease.
For instance, whenever a sick person sneezes or coughs, he/she produces drops of fluid diseased with the cold virus that are transmitted into the environment. If these droplets are breathed into the nose, then the cold virus will settle into the person’s nose.
How long does a cold last? A person can remain contagious for and up to two weeks. It is also possible to transfer a cold infection one or two days before other symptoms appear. But most of the time you remain the most infectious when you are at the height of your symptoms.
Diagnosis of the Common Cold
How to diagnose the common cold? To determine which infectious agent caused the cold, it is better to talk with the patient and inspect the mucous membrane of the throat. The presence of plaque, pustules, and films speaks in favor of the bacterial nature of the cold. If only a hyperemic and swollen throat is noted, it is most likely a viral disease.
To clarify the diagnosis and determine the specific causative agent of colds help laboratory methods of research. It is necessary to conduct a clinical blood test with the determination of COE and leukocyte formula and a swab from the mucous membrane of the pharynx for further microscopy and culture with the determination of sensitivity to antibiotics.
However, suppose your symptoms of a cold vs flu are severe or do not improve after a week. In that case, your doctor may recommend additional tests to rule out other conditions, such as a bacterial infection or allergies. These tests may include throat cultures, rapid antigen tests, and allergy testing. One of the main reasons to get an annual physical exam is to detect potential health issues early and maintain overall wellness.
Treatment Options for the Common Cold
There is no universal method of treating the common cold — it all depends on the causative agent, the symptoms of the disease and its severity, the state of immunity, and the body in general. If the diagnosis of “acute respiratory viral infections” is made, antiviral and symptomatic therapy is carried out, aimed at reducing fever, intoxication, pain, and swelling of the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose.
With an acute cough accompanying ARVI, it is necessary to ensure adequate fluid intake and air humidification. In the appearance of sputum, use drugs with liquefying and expectorant effects.
Anti-inflammatory therapy is also prescribed for acute respiratory bacterial infections with symptoms of the common cold. Against this background, irrigation procedures are carried out—washing the nasal cavity and gargling the throat with solutions. In addition, antibiotics are generally required.
Only a doctor can choose an antibacterial drug. This choice is determined by the sensitivity of microorganisms to the antibiotic and the duration of treatment—indications for the use of a particular drug.
You shouldn’t take antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription. Bacteria can show resistance to the antimicrobial drug, and its use will be not only ineffective but also harmful.
Home Remedies for Cold Relief
Drinking plenty of fluids will help you defeat symptoms of a cold vs flu at an early stage. With the help of liquids, you eliminate toxins and wastes formed in the process of fighting the disease, preventing them from gaining a foothold in the body. Full sleep and rest – are some of the most important conditions for successful treatment. More often than not, it is lack of sleep and lack of proper rest combined with permanent stress that causes the body to capitulate to the cold. The top tips to live a healthy lifestyle help you to be in good shape.
Gargle – an easy and effective method of therapy of infectious and inflammatory diseases, which will help to strengthen the local immunity of the mucosa and prevent the spread of infection deep into the body. Use warm water with the addition of sea salt for this.
Washing the nose with sea salt at the first symptoms of the common cold will help neutralize the infection or at least reduce the intensity of the disease. The therapeutic solution removes pathological secretion from the surface of the mucosa along with viruses, bacteria, allergens and dust, reducing swelling and inflammation.
Preventing the Common Cold
Basic preventive measures are aimed at keeping the immune system working and preventing cold vs flu symptoms. They include:
- rational nutrition;
- regular physical activity;
- washing hands after being outdoors or before eating;
- frequent ventilation of the room;
- avoiding contact with sick people, wearing a mask in public places during epidemics;
- vaccination against influenza.
It is important to maintain the health of the mucous membranes of the nose and throat: do not allow drying, do not abuse vasoconstrictors, do not smoke, and minimize the amount of alcohol. A back-to-school medical check-up is important to ensure children are healthy and up-to-date on their vaccinations.
When to See a Doctor for Cold Symptoms
Sometimes the treatment of a viral disease is out of control at some point, forcing you to resort to emergency medical assistance. Many healthcare providers offer flu treatment services to help reduce symptoms and speed up recovery.
It is strongly recommended to call an ambulance if you notice severe stages of the flu:
- if your temperature rises above the 40˚C mark;
- you have a very high temperature for more than three or four days;
- you have severe painful sensations in the chest area, cramps;
- you have developed a purple-colored rash;
- you do not notice any relief after a week of active treatment of the disease.
It’s also important to visit a doctor if you have concerns about your child’s symptoms of the common cold. Children may be more susceptible to complications from the common cold, such as ear infections or pneumonia. Parents should be aware of the common children viruses that spread easily, especially in school and daycare settings.
Conclusion
The common cold is often an uncomfortable illness. By understanding cold vs flu symptoms and implementing effective home remedies, you can alleviate discomfort and promote faster recovery.
If you’re experiencing persistent or severe symptoms of the common cold don’t hesitate to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. Remember, prevention is key. Practice good hygiene, get adequate rest, and stay hydrated to reduce your risk of contracting the common cold.